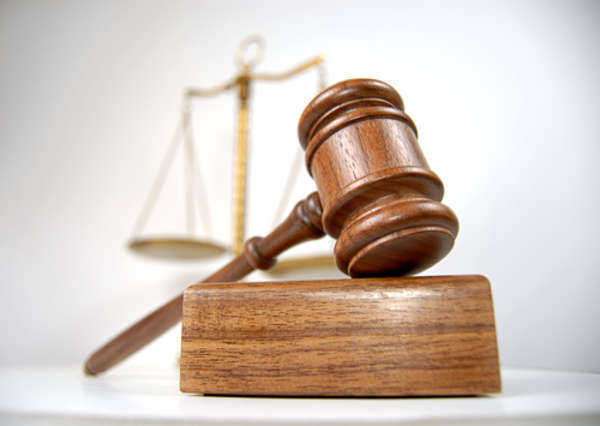
Discover Areas Of Civil Law You Didn’t Know

Discover Areas of Civil Law You Didn’t Know
Civil law governs disputes between individuals and organizations, including contracts, property, business issues, and personal injury claims. While many people are aware of some aspects of civil law, there are many areas that may be new to them. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at some areas of civil law you might not know.
Contract Law
Contract law is one of the most common areas of civil law. It deals with the legal agreements between individuals, companies, and organizations. It covers everything from employment contracts to lease agreements, and they can be complicated to navigate without proper legal counsel.
Environmental Law
This area of civil law deals with the protection of the environment from harm caused by individuals, companies, and organizations. Environmental law covers a wide range of issues, such as clean air, water quality, waste disposal, and land use. With increasing concerns about the impact of human activities on the natural environment, environmental law is becoming more critical than ever.
Intellectual Property Law
Intellectual property law covers the protection of any original works, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights. It gives individuals and organizations the exclusive rights to use their inventions, creative works, or company branding. Intellectual property law is essential for protecting the hard work and creativity of individuals and businesses.
Immigration Law
Immigration law governs the entry, residency, and naturalization of foreign nationals in a country. Whether it’s for work, education, or permanent residency, immigration law is crucial to ensuring that the process is fair and just for all parties involved. Immigration law is continually evolving, and changes in policies and procedures are frequent.
Family Law
Family law deals with all matters related to family relationships, including marriage, divorce, child custody, adoption, and domestic violence cases. It’s an area of law that affects individuals and families on a personal level and can be very emotional. It’s essential to have an experienced family law attorney to guide during these situations.
Personal Injury Law
Personal injury law deals with harm caused to an individual’s mind, body, or emotions due to the negligence or intentional actions of another party. This can include medical malpractice, workplace injuries, automobile accidents, and more. In personal injury cases, the plaintiff seeks compensation for damages, including medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering.
Bankruptcy Law
Bankruptcy law covers the legal process for individuals or businesses struggling with overwhelming debt. It offers a way to eliminate or restructure debt, depending on the individual’s financial circumstances. Bankruptcy cases can be complex and require the expertise of a skilled attorney.
Conclusion
Civil law covers a wide range of disputes, and understanding each area is crucial for individuals and businesses to protect themselves legally. The above areas of civil law that we have discussed are just the tip of the iceberg. Consulting with a knowledgeable attorney can provide you with the advice and representation necessary to navigate the complex world of civil law.
Civil law includes cases that involve an individual bringing a lawsuit against another individual or entity. In criminal cases the state or Federal Government prosecutes an individual for a crime and seeks criminal penalties. In a civil case, however, the individual or entity sues an individual or entity in the hopes of receiving some compensatory award.
Civil cases may include personal injury claims. For example, an individual that falls on a property due to some action or inaction by the owner may attempt to take the case to civil court. Civil court may include small claims of less than five hundred dollars, or large claims in which an individual is seeking several types of compensatory damage awards.
In civil cases, compensatory damages may include damages for injury, including medical bills and lost wages which resulted from that injury.